Understanding Background Reports
Understanding background reports is crucial for making informed hiring decisions and ensuring compliance with regulations. A background report provides valuable insights into an applicant’s past, but deciphering the information can seem complex. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate and interpret these reports.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reading Background Reports
1. Identify Personal Information: Confirm the candidate’s identity by reviewing personal details such as name, date of birth (DOB), address, and social security number.
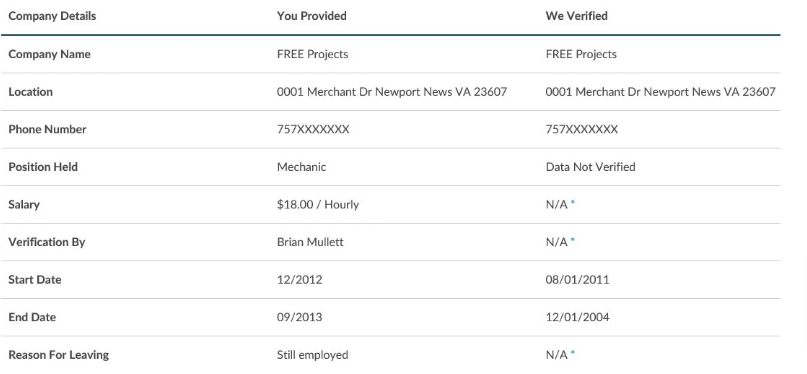
2. Review Employment History: Evaluate the candidate’s work history for consistency and experience (employers, job titles, employment dates, reasons for leaving). Verify this information against the applicant’s resume or cover letter, to check for discrepancies.
3. Examine Education Records: Verify academic credentials like degrees earned, institutions attended, and dates of attendance. Contact schools directly if necessary for further verification.
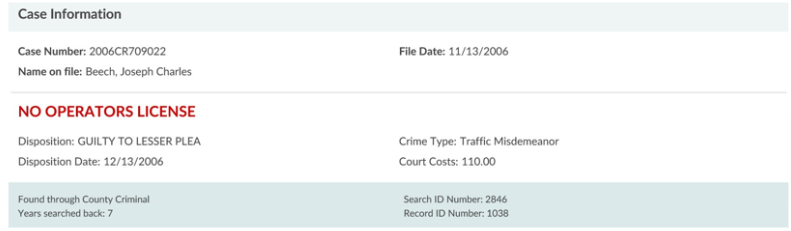
4. Check Criminal Records: Look for any criminal history that might be relevant to the job role (felonies, misdemeanors, and infractions). Consider the nature of the offense, date, and disposition (outcome) of the case.
5. Understand Credit Reports: Review the overall credit score for financial reliability, particularly for roles involving financial duties. Also, look at the types and statuses of credit accounts, and check for any bankruptcies or liens.
6. Motor Vehicle Records (MVR): This section (relevant for driving positions) details driving history, including traffic violations, accidents, and license status.

7. Professional Licenses: Verify the existence and validity of any professional licenses required for the job.
Common Terms and Definitions
Adjudication: The process of reviewing and interpreting background check findings.
Felony: A serious crime, usually punishable by imprisonment for more than one year.
Misdemeanor: A less serious crime, punishable by less than one year of imprisonment.
Disposition: The final outcome of a legal case (e.g., convicted, dismissed).
SSN Trace: A search to verify the validity of a Social Security Number.
Tips and Best Practices
Review the entire report carefully.
Look for inconsistencies or discrepancies.
Always follow a consistent process when reviewing background reports.
Consider the context and relevance of any findings.
Keep abreast of changes in laws and regulations regarding background checks.
Always follow Fair Hiring Practices and avoid discriminatory interpretations.
If you are unsure about an item, seek clarification from the background screening agency.
Benefits of Understanding Background Reports
Understanding background reports can significantly enhance your hiring process by:
Reducing Risks: Ensuring a safe and compliant workplace.
Improving Quality of Hire: Selecting candidates who best fit the company culture and job requirements.
Get Started Today!
For further assistance or clarification on reading and interpreting background reports, contact SimpliVerified. Our team is ready to provide you with the support and guidance you need to navigate background checks with confidence.
